Online knowledge bases have become the foundation of how people learn and verify information today. For over twenty years, Wikipedia has served as a human-edited encyclopedia powered by millions of contributors worldwide. Now, Grokipedia, built using xAI’s Grok language model, is entering the scene with an AI-driven approach to article creation, updates, and fact-checking. It positions itself as a “bias-free” alternative that uses synthetic accuracy instead of human editing.
This shift from human collaboration to machine intelligence raises an important question: can artificial intelligence truly redefine trust, neutrality, and accuracy in online knowledge sharing? The comparison between Grokipedia and Wikipedia reveals how technology is transforming the way we build and believe in digital information.
The Evolution of Online Knowledge Bases
The journey of online knowledge sharing has evolved from community-driven editing to algorithmic intelligence. Wikipedia, launched in 2001, marked a turning point by making knowledge accessible to anyone with an internet connection. It relied on a global network of volunteers who created, edited, and verified information collaboratively. This model empowered collective participation but also introduced challenges such as inconsistency, bias, and the occasional spread of misinformation.
Enter Grokipedia, a next-generation platform that replaces human crowdsourcing with artificial intelligence. Built on the Grok language model, it automatically generates, updates, and fact-checks articles using diverse online sources. This shift reflects a broader transformation in how society values information , prioritizing speed, automation, and perceived neutrality.
The transition from Wikipedia’s human oversight to Grokipedia’s AI automation represents more than a technical upgrade. It signals a new era where the pursuit of truth may rely as much on machine learning as it once did on human collaboration.
Core Differences Between Grokipedia and Wikipedia
Both Grokipedia and Wikipedia share the same purpose of making information accessible to everyone, but the way they work is completely different. Wikipedia depends on people to create and manage content, while Grokipedia uses automated systems to collect and organize knowledge. One is driven by human effort, the other by technology that processes data on its own.
Here’s how they differ at their core:
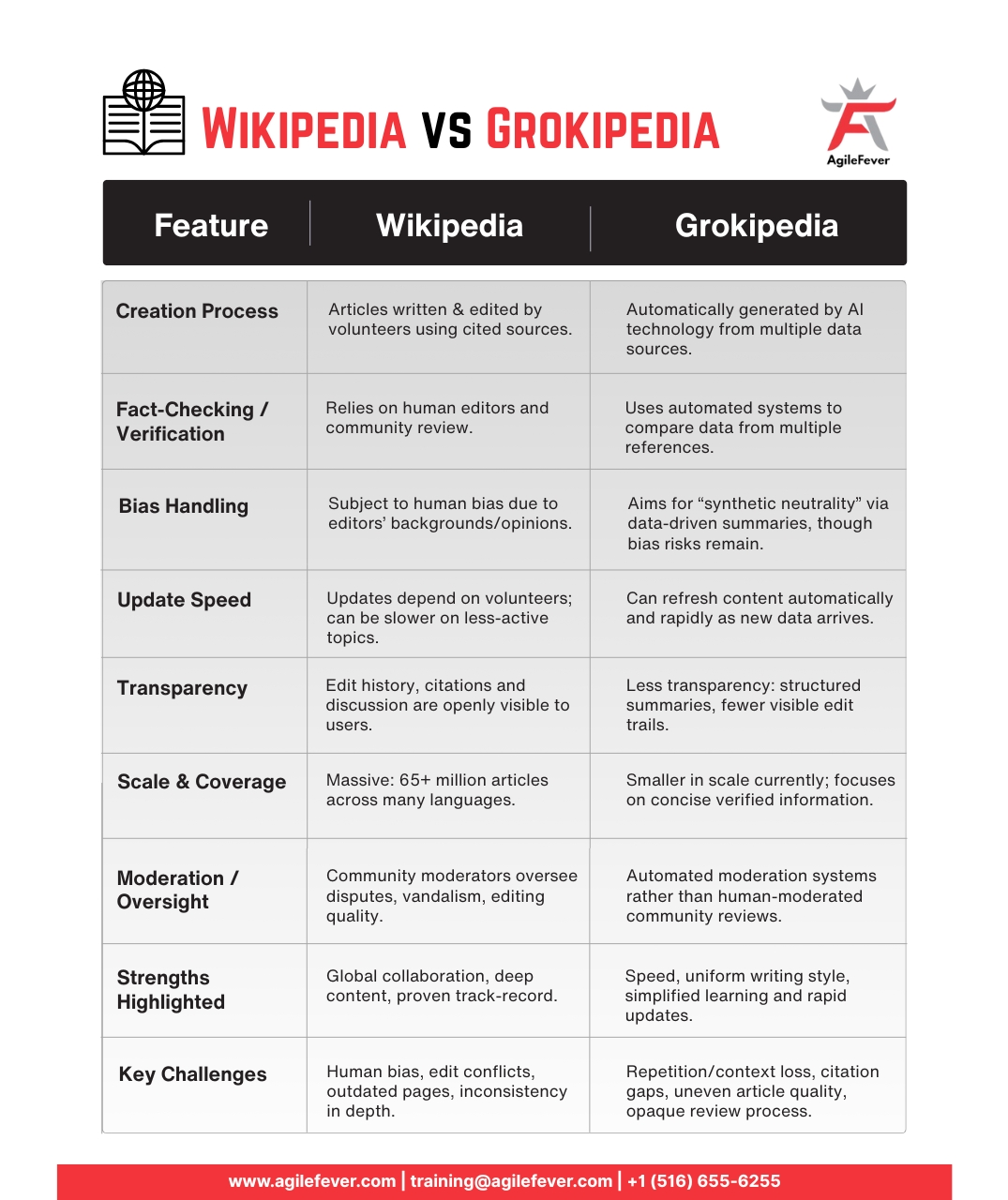
- Creation Process: Wikipedia articles are written and edited by volunteers who rely on credible sources. Grokipedia automatically gathers and compiles information into articles.
- Fact-Checking: Wikipedia relies on editors to review and correct errors. Grokipedia checks content by comparing data from multiple references.
- Bias Handling: Wikipedia may reflect human bias during editing discussions. Grokipedia aims to reduce bias through consistent data-driven summaries.
- Update Speed: Wikipedia updates depend on contributors adding new information. Grokipedia refreshes pages automatically as new data becomes available.
- Transparency: Wikipedia shows edit histories and citations. Grokipedia presents structured summaries with less visibility into its content sources.
- Scale: Wikipedia contains more than 65 million articles in several languages. Grokipedia has fewer pages but focuses on concise and verified information.
- Moderation: Wikipedia uses community moderators to manage disputes. Grokipedia applies automated systems to maintain content accuracy.
In essence, Wikipedia’s strength comes from human collaboration, while Grokipedia represents a more technical, system-based approach to organizing information.
Strengths of Grokipedia
Grokipedia brings a new style of information delivery that focuses on speed, clarity, and consistency. Instead of waiting for editors to review and update pages, it uses automated processes to collect and organize data almost instantly. This helps users get recent and simplified insights on trending or fast-changing topics.
Some of its main strengths include:
- Quick Updates:
Grokipedia can refresh information faster than traditional knowledge bases, making it useful for topics that evolve daily.
- Uniform Writing Style:
Since all entries follow a structured format, readers experience consistent tone, layout, and readability across pages.
- Simplified Learning:
Articles are concise and easy to scan, allowing users to understand complex subjects without lengthy explanations.
- Fewer Biases:
By gathering information from various sources, Grokipedia tries to maintain a neutral point of view across sensitive topics.
- Fact Verification Tags:
Each entry shows when it was last verified, helping users trust the content’s freshness and accuracy.
While still developing, Grokipedia demonstrates how automation can make large-scale knowledge management faster and more reliable. It reflects how technology is shifting from human-edited encyclopedias toward systems that deliver data-driven summaries with minimal manual effort.
Strengths of Wikipedia
Wikipedia remains one of the most trusted sources of information on the internet because of its open and human-centered structure. It has built a reputation for reliability through years of community involvement and transparent content moderation. Every edit, source, and discussion is visible to the public, giving readers a clear understanding of how information is formed and corrected.
Some of its main strengths include:
- Global Collaboration: Millions of volunteers contribute to Wikipedia, ensuring diverse viewpoints and knowledge from different regions and cultures.
- Transparency and Accountability: Every article has an edit history and cited references, allowing anyone to verify the source of information.
- Depth of Content: With more than 65 million articles, Wikipedia covers a massive range of topics with detailed explanations and historical context.
- Proven Track Record: Over two decades of public use and editorial oversight have made it one of the most stable and credible online knowledge sources.
- Community Moderation: Disputes or errors are openly discussed and corrected by editors, maintaining a balance between accuracy and inclusivity.
Wikipedia’s greatest strength lies in its human touch. The combination of open collaboration, constant feedback, and visible sourcing has helped it stay relevant even in an era of automated information systems.
The Debate Around Bias and Trust
One of the most important differences between Grokipedia and Wikipedia lies in how each handles bias and trust. Both platforms aim to present factual information, yet their methods reflect different ideas of neutrality.
Wikipedia depends on community editing, which means articles are influenced by the backgrounds, opinions, and interpretations of contributors. While this encourages discussion and correction, it can also introduce bias, especially on political or cultural topics. Disputes between editors sometimes shape how facts are presented, making neutrality a constant challenge.
Grokipedia, on the other hand, promotes the idea of “synthetic neutrality.” Instead of relying on personal judgment, it compiles information from multiple sources and balances perspectives through data comparison. However, complete neutrality is difficult to achieve even in automated systems. The technology that powers Grokipedia still learns from existing data, which may already contain hidden bias or inaccuracies.
When it comes to trust, people often rely on what they can see. Wikipedia’s open edit history and visible citations give users confidence in how information is built. Grokipedia’s machine-based process is faster but less transparent, leaving users to trust the system’s unseen logic.
The debate between these two approaches highlights a deeper question: should trust in knowledge come from human oversight or from technical precision?
Content and Technical Challenges
Both Grokipedia and Wikipedia face unique challenges in creating, managing, and verifying large volumes of information. Their difficulties come from the systems that power them, automation for Grokipedia and human participation for Wikipedia.
Challenges for Grokipedia:
- Repetition and Context Loss: Automated summaries can repeat existing text or overlook deeper meaning within topics.
- Citation Gaps: Some entries may lack proper references or detailed sources, affecting verification.
- Limited Search Features: Finding specific information or related topics can be harder compared to traditional encyclopedias.
- Uneven Article Quality: Some subjects are covered in detail, while others remain brief or incomplete.
- Opaque Review System: Without visible editorial oversight, users cannot see how information is verified or corrected.
Challenges for Wikipedia:
- Human Bias: Personal opinions or interpretations can influence how facts are presented.
- Edit Conflicts: Disagreements between contributors may lead to repeated changes or temporary misinformation.
- Outdated Pages: Articles that attract less attention often go long periods without updates.
- Inconsistent Depth: Some pages contain extensive research, while others are minimal or overly simplified.
- Vandalism Risks: Open editing allows users to make unverified or misleading edits.
Both platforms highlight the same truth: building a trustworthy knowledge base requires balancing automation, community input, and quality control.
The Future of Knowledge Sharing
The comparison between Grokipedia and Wikipedia reflects a broader transformation in how people create and consume knowledge. As technology advances, the line between human insight and automated processing continues to blur, shaping the future of how information will be built, verified, and trusted.
Emerging Directions in Knowledge Platforms:
- Blending Human and Machine Input:
Future systems may combine Wikipedia’s collaborative model with Grokipedia’s automated analysis to create faster, more accurate, and community-reviewed knowledge sources.
- Real-Time Information Updates:
Automated platforms will likely lead the way in instant updates for breaking topics, scientific research, and current events.
- Enhanced Verification Systems:
Transparent tagging of data sources, verification timestamps, and citation tracking could make both human and automated platforms more credible.
- Personalized Knowledge Delivery:
AI tools may soon adjust how information is presented based on user behavior, interests, or expertise level.
- Ethical Responsibility in Content Creation:
Both models must find ways to reduce misinformation, ensure source accuracy, and promote transparency in how facts are chosen and shared.
In the future, the most trusted knowledge bases will not rely entirely on people or machines. They will depend on collaboration between the two, combining human understanding with the precision and scale of automated systems.
Conclusion
The rise of Grokipedia and Wikipedia shows two different paths toward the same goal of accessible, trustworthy knowledge. Wikipedia relies on human collaboration and open editing, while Grokipedia focuses on automation and speed. Both have unique strengths that shape how we learn and share information online. The future of knowledge will depend on how effectively people and technology work together to ensure accuracy and fairness in what we read. Join our AgileFever Masterclass for free and explore how AI and innovation are transforming the way we create and consume knowledge.